Stage 1: Foundation and Establishment of the Business Model (1987-Early 1990s)
In 1987, Morris Chang founded TSMC with funding from the Taiwan government and Philips. The most critical decision was establishing the Pure-play Foundry business model.
- Founding Background: At that time, most semiconductor companies designed and manufactured their own chips (IDM model).
- Core Shift: TSMC promised not to design its own products, ensuring it would never compete with its customers.
- Key Event: Founded in 1987. In 1988, the company received certification and orders from then-Intel CEO Andy Grove, establishing a firm foothold in the international market.
Revenue Level: During this period, revenue grew from 100 million NTD at the time of founding to approximately 19.3 billion NTD in 1994.
Core Technologies: 1.Pure-play Foundry Model: This was the most central business innovation, promising never to compete with customers. 2.Process Introduction: Early introduction of 2-micron and 1-micron processes, and passing Intel’s rigorous certification in 1988 to prove foundry quality.
Stage 2: Technological Catch-up and Rapid Expansion (Mid-1990s-Mid-2000s)
With the rise of fabless semiconductor companies like Qualcomm, NVIDIA, and MediaTek, demand for foundry services surged. During this stage, TSMC began transitioning from a follower to a leader.
- Capital Markets: Listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange in 1994 and on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in 1997.
- Independent R&D: Developed 0.13-micron autonomous technology in 2003, breaking dependence on foreign technology licensing.
- Technical Breakthrough: During this period, TSMC decided to invest in Immersion Lithography, which became a key turning point for surpassing competitors later on.
Revenue Level: Revenue leaped from the 30 billion NTD level to around 330 billion NTD in 2008, officially joining the ranks of top-tier global semiconductor companies.
Core Technologies: 1.0.13-micron Autonomous Process: The successful development of the 0.13-micron technology with all-copper interconnects in 2003 was the key point where TSMC broke away from technology licensing and moved toward complete self-reliance. 2.Immersion Lithography: Led by Dr. Burn Lin, this technology used the refractive properties of water to shorten wavelengths, allowing TSMC to leapfrog the then-leader IBM at the 65nm node and become the industry rule-setter.
Stage 3: Advanced Process Leadership and the Mobile Revolution (2010-2019)
The explosion of smartphones led TSMC into a period of high growth. Morris Chang returned as CEO in 2009 and significantly increased R&D investment to ensure absolute leadership in advanced processes.
- Apple Orders: Began producing A-series chips for Apple in 2014 and became the exclusive supplier after 2016.
- Surpassing Competitors: Achieved massive success with 28nm and 7nm processes, significantly increasing market share.
- Essential Technology: Pioneered the commercial use of Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, further consolidating its competitive advantage.
Revenue Level: Revenue entered a period of explosive growth, doubling from the 300 billion NTD level to surpass the 1 trillion NTD mark in 2019.
Core Technologies: 1.FinFET (Fin Field-Effect Transistor): Successful commercialization of three-dimensional transistor structures at the 16nm node, solving power leakage issues. 2.HKMG (High-k Metal Gate): Significantly improved chip performance and reduced power consumption, establishing 28nm as the longest-lasting and most successful process node in history. 3.EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography): TSMC led the world in mass-producing EUV during the 7nm enhancement stage, which is currently the only path for manufacturing cutting-edge chips.
Stage 4: Geopolitics and AI-Led Global Expansion (2020-Present)
TSMC has been hailed as the “Silicon Shield” (Guardian Mountain of the Nation), becoming a strategic asset under global geopolitical tensions.
- AI Wave: Demand for AI chips skyrocketed starting in 2023. Major players like NVIDIA have immense demand for TSMC’s advanced processes (4nm, 3nm) and advanced packaging (CoWoS).
- Global Layout: Began establishing fabs in Arizona (USA), Kumamoto (Japan), and Germany, transforming from a local enterprise into a truly global production system.
- Process Evolution: Mass production of 3nm began in late 2022, with 2nm expected to enter mass production in 2025.
Revenue Level: Revenue showed a steep upward slope, growing rapidly from 1.3 trillion NTD to nearly 2.8 trillion NTD in 2024, with profitability also hitting record highs.
Core Technologies: 1.3nm and 2nm Processes: 3nm is already in full mass production, and the all-new GAA (Gate-all-around) architecture is expected to be introduced at 2nm to maintain technical leadership at physical limits. 2.CoWoS Advanced Packaging: An indispensable technology for current AI chips (such as NVIDIA products). Through 2.5D or 3D stacking, it allows chip-to-chip transmission bandwidth and efficiency to reach extreme levels. 3.3D Fabric Integration Platform: Combines front-end processes with back-end packaging to provide customers with a one-stop chip integration solution.
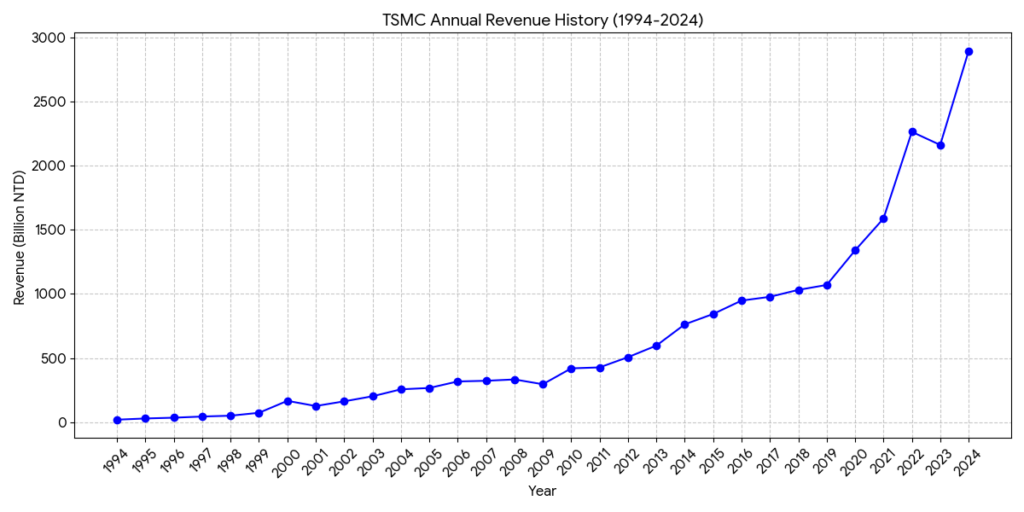
This chart illustrates the exponential growth of TSMC since its listing on the Taiwan Stock Exchange. The revenue has surged from 19.34 billion NTD in 1994 to 2,894.31 billion NTD (approximately 2.89 trillion NTD) in 2024.
Several key growth inflections can be identified from the trend:
- Smartphone Era (2010-2019): The demand for mobile processors (e.g., Apple A-series chips) propelled revenue past the 1 trillion NTD milestone.
- AI and HPC Surge (2020-Present): Driven by cloud computing and the generative AI boom starting in late 2023, the revenue curve has become significantly steeper, nearly doubling within just four years.
Sources:
