The history of Microsoft can be categorized into five distinct eras, defined by leadership changes and strategic pivots.
1. The Founding and the MS-DOS Breakthrough (1975–1985)
- 1975: Bill Gates and Paul Allen founded Microsoft in Albuquerque.
- 1980: The pivotal deal with IBM. Microsoft provided the operating system (MS-DOS) for the IBM PC but retained the right to license it to other manufacturers.
- 1983: Paul Allen left the company due to health reasons.
Business Development: The core strategy was the “per-processor licensing” model adopted in the early 1980s. Regardless of whether hardware manufacturers installed MS-DOS, they had to pay a royalty to Microsoft for every computer sold. This effectively sidelined early competitors like Digital Research.
Financial Milestones:
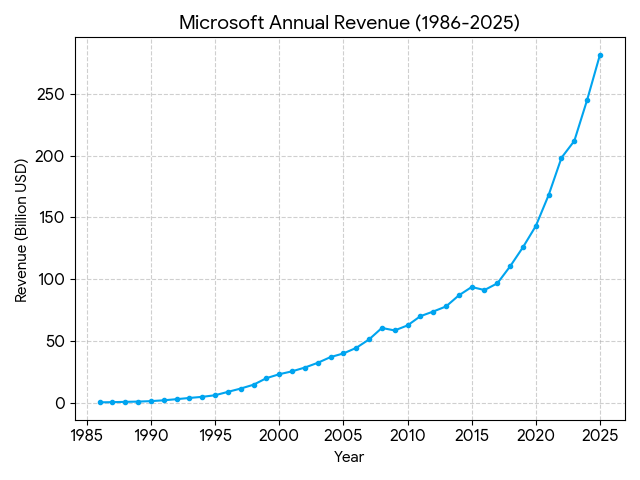
- 1975 First Year Revenue: 16116 USD.
- 1985 Revenue: 140 million USD.
- By 1985, international revenue accounted for over 30% of total revenue, demonstrating early global expansion capabilities.
2. IPO and the Windows Dominance (1986–2000)
- 1986: On March13, Microsoft went public (IPO) at 21 USD per share. By the end of the day, the stock rose to 28 USD, making Bill Gates one of the wealthiest people in the world.
- 1990: Launch of Windows3.0 and the first Microsoft Office suite.
- 1995: Launch of Windows95. It featured the Start menu and bundled Internet Explorer, sparking the “Browser Wars.”
- 1998: The US Department of Justice filed an antitrust lawsuit against Microsoft regarding its monopoly power.
Business Development: Massive resources were invested in development tools like Visual Basic to ensure third-party software was developed for Windows first, building a powerful platform ecosystem. In 1993, the launch of Windows NT officially extended the business footprint from personal PCs to the enterprise server market.
Financial Milestones:
- 1986 Revenue: 197 million USD (Year of IPO).
- 1990 Revenue: 1.18 billion USD (First time exceeding the 1 billion USD mark).
- 2000 Revenue: 22.96 billion USD.
- Stock Performance: Between 1987 and 1999, the stock underwent 8 splits, significantly increasing the share count for original investors.
3. The Ballmer Era and Diversification (2000–2014)
- 2000: Steve Ballmer became CEO; Bill Gates shifted focus to the Gates Foundation.
- 2001: Launch of Windows XP and the first Xbox console.
- 2009: Launch of Bing to compete with Google Search.
- 2010: Launch of Azure, marking the company’s early entry into cloud computing.
- 2011: Acquisition of Skype for 8.5 billion USD.
- 2012: Launch of the Surface tablet, Microsoft’s first major move into PC hardware.
Business Development: Introduced the Enterprise Agreement (EA) to lock large corporations into long-term software contracts, ensuring stable cash flow. In 2009, the search business was rebranded as Bing to challenge Google’s advertising revenue model.
Financial Milestones:
- 2005 Revenue: 39.79 billion USD.
- 2010 Revenue: 62.48 billion USD.
- 2014 Revenue: 86.83 billion USD.
- Cash Management: In 2004, a special dividend of 3 USD per share was issued, distributing approximately 32 billion USD in cash to shareholders at once.
4. The Nadella Revolution: Cloud First (2014–2022)
- 2014: Satya Nadella took over as CEO with a “Mobile First, Cloud First” strategy.
- 2016: Acquisition of LinkedIn for 26.2 billion USD.
- 2018: Acquisition of GitHub, signaling a major embrace of the open-source community.
- 2021: Launch of Windows11.
- Under Nadella, Microsoft shifted Office to a subscription model (Microsoft365) and grew Azure into a market leader.
Business Development: Broke the “Windows-centric” dogma by bringing Office to iPad and Android devices. Launched industry-specific cloud solutions for sectors like healthcare and retail, increasing Azure’s Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) and stickiness in the B2B segment.
Financial Milestones:
- 2018 Revenue: 110.36 billion USD (First time exceeding the 100 billion USD mark).
- 2022 Revenue: 198.27 billion USD.
- Valuation Recovery: As the business transitioned to a subscription model, Wall Street saw the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio rise from the mid-teens to over 30x.
5. The AI Era (2023–Present)
- 2023: Microsoft announced a multi-billion dollar investment in OpenAI.
- 2023: Integration of GPT-4 technology into Bing and the launch of Microsoft Copilot.
- 2024: Microsoft became the world’s most valuable public company, surpassing a 3 trillion USD market cap, driven by its leadership in Generative AI.
Business Development: Much of the investment in OpenAI was provided via Azure cloud credits, ensuring capital flowed back into Microsoft’s own infrastructure. Launched the Model-as-a-Service (MaaS) model, allowing enterprises to call models via API and converting AI tech into cloud consumption revenue.
Financial Milestones:
- 2024 Fiscal Year Revenue: 245.12 billion USD.
- 2025 Fiscal Year Revenue: 281.72 billion USD (Approx. 15% annual growth).
- Capital Expenditure: To meet AI demand, quarterly Capital Expenditure (CapEx) has scaled to over 10 billion USD.
Sources:
