Here is a summary of the history of Goldman Sachs, broken down into its key evolutionary stages:
Phase 1: The Commercial Paper Pioneer (1869–1906)
- Foundation (1869): Marcus Goldman, a German immigrant, started a small business in a basement in Lower Manhattan. His primary business was buying promissory notes (commercial paper) from local merchants and selling them to banks.
- A Family Partnership (1882–1885): Marcus invited his son-in-law, Samuel Sachs, to join the firm. The company officially became Goldman Sachs & Co. in 1885.
- Connecting Main Street to Wall Street: They revolutionized the market by providing short-term financing to small businesses that were overlooked by the massive commercial banks of that era.
Core Strategy: Niche Market Entry. The firm focused on purchasing short-term promissory notes (commercial paper) from small businesses that were ignored by large banks, building a high-volume network.
Revenue Level: Modest but Stable. Revenue was derived entirely from the narrow spread (interest differential) of trading local business notes.
Operational Focus: Speed and localized credit assessment in the Manhattan business district.
Phase 2: From Notes to IPOs (1906–1930)
- Entry into Underwriting (1906): Led by Henry Goldman, the firm managed its first major Initial Public Offering (IPO) for United Cigar Manufacturers, followed by Sears, Roebuck and Co. This was a shift from debt to equity.
- The 1929 Crash: The firm nearly collapsed during the Great Depression due to the failure of the Goldman Sachs Trading Corp, a highly leveraged investment trust. This disaster severely tarnished the firm’s reputation for years.
Core Strategy: Asset Securitization. Pioneered IPOs for retail and consumer-oriented companies (e.g., Sears, Roebuck), shifting the industry focus away from heavy rail debt.
Revenue Level: High Volatility. Revenue surged during the 1920s bull market but evaporated after the 1929 crash, leading to near-total capital loss.
Operational Focus: Expanding into equity underwriting and leveraged investment trusts.
Phase 3: The Weinberg Era & Reputation Recovery (1930–1969)
- Sidney Weinberg’s Leadership: Often called “Mr. Wall Street,” Weinberg rebuilt the firm’s credibility. He shifted the focus toward long-term client relationships and corporate advisory.
- Ford Motor Company IPO (1956): This was the largest IPO in history at the time. Its success cemented Goldman Sachs as a top-tier investment bank and signaled its full recovery from the 1929 stigma.
Core Strategy: Reputation Rebuilding. Established the “Business Principles,” prioritizing client interests over short-term firm profits to regain trust post-Depression.
Revenue Level: Steady Growth. Revenue was driven by high-profile underwriting fees (e.g., Ford Motor Co.) and corporate advisory services.
Operational Focus: Building long-term relationships with blue-chip American corporations.
Phase 4: Modernization and Global Expansion (1969–1999)
- Trading Dominance (1970s): Under Gus Levy, the firm pioneered “block trading,” allowing institutional investors to trade massive amounts of stock efficiently.
- Acquisition of J. Aron (1981): This acquisition moved the firm into commodities and currency trading, which would later become a massive profit engine (Fixed Income, Currencies, and Commodities – FICC).
- The End of the Partnership (1999): After decades of debate, Goldman Sachs ceased being a private partnership and went public on the NYSE (Ticker: GS). This provided the capital needed to compete with larger global rivals.
Core Strategy: Risk-Taking and Global Expansion. Leveraged the firm’s capital for market-making (Block Trading) and entered commodities through the acquisition of J. Aron.
Revenue Level: Explosive Growth. Revenue reached the multi-billion dollar mark, fueled by the 1980s M&A boom and the rise of the FICC (Fixed Income, Currencies, and Commodities) division.
Operational Focus: Transitioning from a private partnership to a global public company (IPO in 1999).
Phase 5: The Post-Crisis & Digital Era (2000–Present)
- The 2008 Financial Crisis: To survive the liquidity crisis, Goldman converted into a Bank Holding Company, allowing it access to the Federal Reserve’s discount window. It received $10 billion in TARP funds (repaid in 2009).
- Regulatory Shift: Following the crisis and the Volcker Rule, the firm scaled back proprietary trading and leaned more into asset management and advisory.
- Marcus and Digital Expansion (2016–Present): The firm launched Marcus by Goldman Sachs, its first foray into retail consumer banking, aiming to diversify revenue beyond volatile institutional trading.
Core Strategy: Revenue Diversification. Transitioned to a Bank Holding Company in 2008 to ensure liquidity. Later expanded into consumer banking (Marcus) to offset volatile trading income.
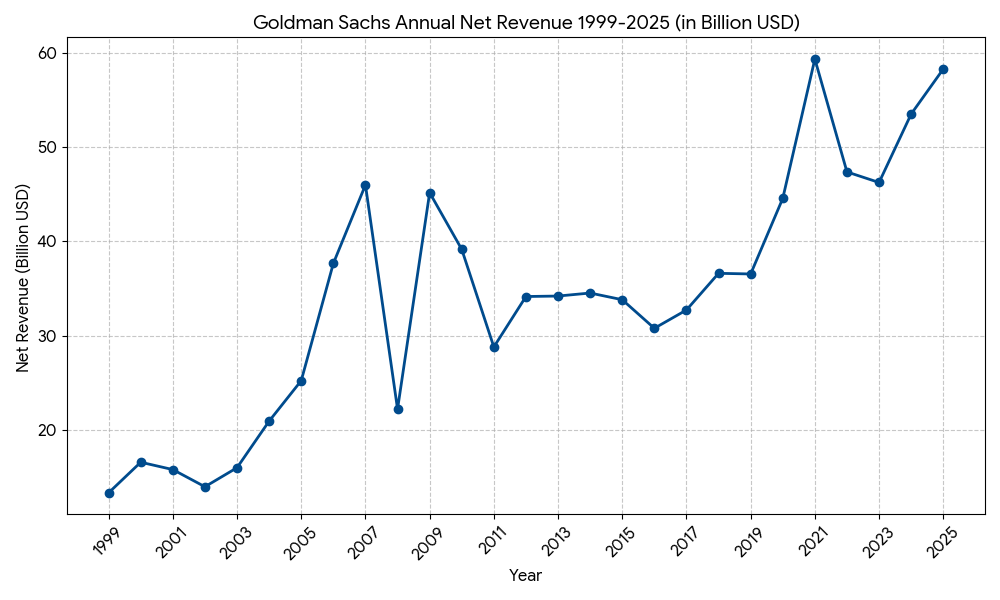
Revenue Level: Massive Scale (40B-50B+ Range). While trading remains a major driver, the firm has significantly increased recurring revenue from Asset and Wealth Management.
Operational Focus: Balancing traditional high-end advisory with technology-driven retail financial services.
In 2026, Goldman Sachs (GS) has pivoted back to its roots, focusing on its high-margin “Elite Investment Banking” DNA after scaling back its consumer banking ambitions (such as the exit from the Apple Card partnership). Its competitive landscape is defined by three distinct tiers:
1. Peer Group Segmentation
| Category | Key Rivals | Competitive Focus |
| The “Universal” Giants | JPMorgan Chase (JPM), Bank of America (BAC) | They possess massive deposit bases and lower funding costs, allowing them to cross-sell lending products that GS cannot match in scale. |
| The Strategic Rival | Morgan Stanley (MS) | The “Battle of the Titans.” While GS leads in trading and M&A, MS has a much larger and more stable Wealth Management engine ($5T+ AUM). |
| The Boutique Specialists | Evercore (EVR), Lazard (LAZ) | These firms compete purely on intellectual capital for M&A advisory without the conflict of interest of a large balance sheet. |
2. Core Competitive Strengths (The Moat)
- Dominance in Mega-Deals: As of early 2026, Goldman Sachs maintains the #1 or #2 global market share in M&A advisory. They remain the “first call” for complex, multi-billion dollar cross-border transactions.
- Institutional Client Services (ICS): GS possesses one of the most sophisticated trading platforms in the world. Their ability to provide liquidity and risk management to hedge funds and asset managers remains unparalleled.
- AI Integration (Project GS 3.0): Unlike peers with legacy retail infrastructure, GS has aggressively integrated generative AI into its investment banking workflow, significantly reducing the time required for due diligence and financial modeling.
3. Strategic Weaknesses & Risks
- Revenue Volatility: Because GS lacks a massive commercial/retail bank (unlike JPM), its earnings are more sensitive to capital market cycles. If IPO and M&A activity slows down, GS feels the impact more acutely than its diversified peers.
- Wealth Management Gap: While GS is growing its Ultra-High-Net-Worth (UHNW) advisory, it still lags significantly behind Morgan Stanley in recurring fee-based revenue from mass-affluent wealth management.
- The “Apple Exit” Hangover: The process of offloading its credit card portfolios to partners like JPMorgan involves significant operational costs and short-term earnings drag through 2026.
4. 2026 Comparative Performance Outlook
| Metric (Est. 2026) | Goldman Sachs (GS) | Morgan Stanley (MS) | JPMorgan (JPM) |
| Return on Equity (ROE) | ~14-16% | ~15-17% | ~17-18% |
| Primary Strength | FICC & Equity Trading | Wealth Management | Global Commercial Banking |
| 2026 Strategy | “Back to Basics” | Scaling Technology | AI-First Banking |
The current market sentiment in 2026 views Goldman Sachs as the “purest play” on a rebounding capital market. With global M&A volumes expected to rise significantly this year, GS is positioned to capture the highest percentage of fee growth among its peers.
In 2026, the Global Banking & Markets (GBM) division remains the crown jewel of Goldman Sachs, generating nearly 70% of the firm’s total revenue. This segment combines the high-stakes world of Investment Banking (Advisory & Underwriting) with Global Markets (FICC & Equities Trading).
1. Competitive Positioning: The “Pure-Play” Elite
Goldman’s primary competitive advantage is its “First Call” status. When a CEO plans a transformative merger or a major sovereign fund needs to move massive liquidity, GS is typically the first point of contact.
- Advisory Dominance: As of early 2026, GS maintains the #1 position in global M&A league tables. Their expertise in “Mega-Deals” (>$10B) provides a brand premium that competitors find difficult to replicate.
- Institutional Client Services (Trading): GS operates one of the world’s most sophisticated market-making engines. In 2026, they have heavily leveraged AI to tighten spreads and provide better pricing in volatile markets, particularly in FICC (Fixed Income, Currencies, and Commodities).
- Capital Efficiency: Having pivoted away from consumer banking, GS has reallocated capital back to GBM, allowing for more aggressive participation in institutional financing.
2. Rivalry Matrix (2026 Context)
| Competitor | Strategic Threat | Competitive Dynamic |
| JPMorgan Chase (JPM) | Balance Sheet Scale | JPM uses its massive $4T+ balance sheet to offer cheap loans as a “hook” for underwriting mandates, a tactic known as “Pay-to-Play” that GS must counter with superior advice. |
| Morgan Stanley (MS) | Equity Capital Markets | MS is the closest rival in Equities and IPOs. However, MS has shifted focus heavily toward Wealth Management, leaving GS as the primary “Pure-Play” investment bank. |
| Evercore / Centerview | Independence | These boutiques win clients by offering advice free from the conflicts of interest (like lending or trading) that large banks face. |
| Blackstone / Apollo | Private Credit | In 2026, these “Shadow Banks” are increasingly competing with GS for corporate lending and restructuring deals through private debt funds. |
3. Key Drivers & Trends for 2026
- The M&A Supercycle: After a period of high interest rates, 2026 is seeing a “catch-up” period for mergers. GS is the primary beneficiary of this volume surge due to its deep sector coverage in Tech, Healthcare, and Energy.
- AI-Enhanced Dealmaking: GS has deployed “Project GS 3.0,” utilizing generative AI to automate the first 40% of the investment banking “pitch book” process. This allows their bankers to focus more on high-level strategy rather than data entry.
- Financing Modernization: With the rise of Private Credit, GS’s GBM division is increasingly acting as an intermediary, connecting corporate borrowers with private lenders, earning fees without necessarily putting its own capital at risk.
4. Critical Challenges (The “Beats” GS must watch)
- Regulatory Capital (Basel III End-Game): Higher capital requirements in 2026 limit the amount of leverage GS can use in its trading business, which can compress Return on Equity (ROE).
- Geopolitical Fragmentation: As markets become more localized, GS faces challenges from regional champions in Europe and Asia (like HSBC or Nomura) that have deeper local government ties.
- Talent Wars: The rise of private equity and hedge funds continues to drain top-tier MD (Managing Director) talent away from traditional banks like GS.
Summary
In 2026, Goldman Sachs’ GBM division is successfully executing a “Back to Basics” strategy. By exiting retail banking, the firm has sharpened its focus on being the world’s premier financial architect. While it lacks the sheer size of JPMorgan, its agility and technical execution in trading and advisory remain the industry gold standard.
Sources:
Dealogic M&A League Tables 2026: https://www.dealogic.com/
Goldman Sachs 2026 Global Outlook: https://www.goldmansachs.com/insights/
Goldman Sachs 2026 Strategic Update: https://www.goldmansachs.com/investor-relations/
Morgan Stanley Wealth Management Report 2026: https://www.morganstanley.com/about-us/investor-relations
Back to Goldman Sachs page
