The history of Samsung can be categorized into four distinct stages, evolving from a small trading company into a global technology powerhouse.
Stage 1: Foundation and Diversification (1938–1960s)
In 1938, Lee Byung-chul founded Samsung Sanghoe in Daegu, Korea. It started as a small trading company exporting dried fish, vegetables, and noodles to China.
- 1950s: After the Korean War, Samsung focused on national reconstruction. It established Cheil Jedang (sugar refining) and Cheil Industries (wool), leading South Korea’s import substitution industrialization.
- 1960s: The group expanded into finance, insurance, and department stores, growing into a major chaebol (conglomerate).
During this foundational period, Samsung was not yet a high-tech company. Its core technologies resided in food processing (sugar refining), textile manufacturing (wool), and logistics. This era focused on capital accumulation through essential consumer goods.
- Revenue Level: Samsung operated as a prominent domestic trading house. Revenue was derived almost entirely from the Korean market. While it was a leading firm within South Korea, its financial scale remained small compared to international industrial giants of the time.
Stage 2: Entry into Electronics and Heavy Industry (1969–1987)
This era marked the shift toward the technology sector that defines the brand today.
- 1969: Samsung Electronics was established. It initially produced black-and-white televisions through a joint venture with Sanyo.
- 1970s: The company expanded into shipbuilding, petrochemicals, and heavy machinery.
- 1983: In a high-risk move, Lee Byung-chul announced that Samsung would enter the semiconductor industry, successfully developing 64K DRAM chips.
Samsung shifted its focus to electronics and heavy industry. Core technologies evolved from the assembly of black-and-white and color televisions to shipbuilding and petrochemicals. A historic milestone occurred in 1983 when Samsung mastered the design and production of 64K DRAM.
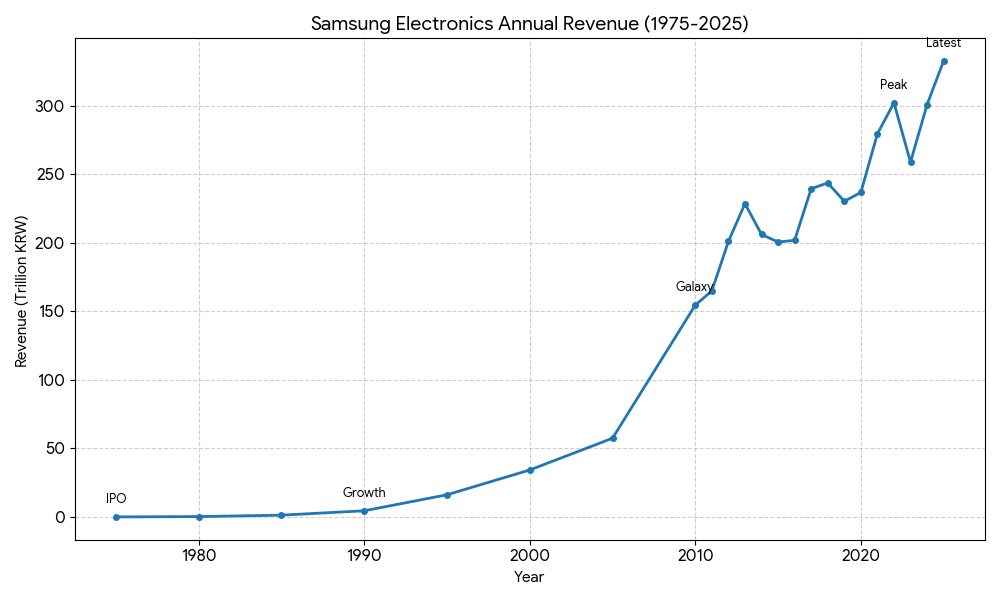
- Revenue Level: Samsung Electronics’ annual revenue surpassed 100 million USD in the late 1970s. By 1984, driven by the export of home appliances and the early success of semiconductor components, revenue reached approximately 1.3 trillion KRW.
Stage 3: The New Management Era and Global Expansion (1987–2010s)
After Lee Byung-chul’s death in 1987, his son Lee Kun-hee took leadership and initiated a total cultural transformation.
- 1993: Lee Kun-hee announced the “New Management” philosophy in Frankfurt, famously telling employees to “change everything except your wife and children.” The focus shifted from quantity to high-end quality.
- 1990s–2000s: Despite the Asian Financial Crisis, Samsung focused on core technologies. It became the world leader in memory chips and LCD panels.
- 2005: Samsung surpassed Sony to become the world’s most popular consumer electronics brand.
This stage was defined by the New Management initiative. Core technologies centered on DRAM and NAND Flash memory, TFT-LCD panels, and CDMA mobile communication. Samsung transitioned from a fast follower to a global leader, becoming the world’s top memory chip maker in 1992.
- Revenue Level: Revenue experienced explosive growth. From approximately 4.5 trillion KRW in 1990, the company surged to 136 trillion KRW (about 117 billion USD) by 2009, surpassing many global competitors to become the world’s largest technology company by sales.
Stage 4: Mobile Dominance and Future Frontiers (2010–Present)
Under the leadership of Jay Y. Lee, Samsung transitioned into the smartphone and AI era.
- 2010: The launch of the Galaxy S series established Samsung as the primary competitor to Apple and eventually the world’s largest smartphone manufacturer.
- 2020s: The company is now prioritizing “Future Growth Engines,” including 5G, Foldable technology, AI, and advanced 3nm semiconductor foundry processes.
Core technologies shifted toward AMOLED displays, Exynos mobile processors, and the Galaxy smartphone ecosystem. In semiconductors, Samsung pioneered EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet) lithography and GAA (Gate-All-Around) architecture for 3nm logic chips.
- Revenue Level: Annual revenue consistently stayed above the 200 trillion KRW mark. In 2022, the company hit a record high of 302.2 trillion KRW. Despite a downturn in the chip market in 2023, revenue recovered to approximately 301 trillion KRW in 2024 as demand for high-end components returned.
Future and Current Focus: The AI and Next-Gen Component Era (2025–2026)
As of early 2026, core technologies are focused on HBM (High Bandwidth Memory) for AI servers, 2nm advanced foundry processes, and on-device AI integration (Galaxy AI). Samsung is leveraging the AI boom to integrate its semiconductor prowess with its vast array of consumer devices.
- Revenue Level: According to financial reports from January 2026, Samsung’s revenue has reached new heights due to the massive demand for AI-related chips. Quarterly revenue for Q4 2025 is estimated at 93 trillion KRW, with annual figures projected to set new historical benchmarks.