The history of Eli Lilly and Company can be divided into several transformative eras:
1. Founding and Standardization (1876-1900s)
Colonel Eli Lilly, a chemist and Civil War veteran, founded the company in 1876 in Indianapolis. At a time when many medicines were unreliable, he committed to scientific rigor.
- 1876: Introduced Quinine to treat malaria.
- 1886: Hired the first full-time scientist to focus on formal research and development.
- Innovation: Developed gelatin-coating for pills and capsules to make them easier to swallow.
2. The Insulin Revolution (1920s-1940s)
Lilly transitioned from a local manufacturer to a global leader by mastering the mass production of biological medicines.
- 1923: Partnered with Banting and Best from the University of Toronto to market Iletin, the world’s first commercial insulin for diabetes.
- 1940s: Became one of the first companies to mass-produce Penicillin during WWII and later helped produce the Salk polio vaccine.
Key Deals:
- 1922 Licensing Agreement: Partnered with the University of Toronto for the exclusive rights to manufacture Insulin. This is the most pivotal deal in company history, transforming Lilly into a global powerhouse.
3. The Antibiotic and Expansion Era (1950s-1970s)
Lilly became a powerhouse in infectious diseases, discovering and manufacturing several classes of antibiotics.
- 1950s: Launched Vancomycin and Erythromycin.
- 1960s: Introduced Cephalosporins, a major breakthrough in antibiotic therapy.
- Diversification: Briefly expanded into agricultural chemicals and animal health (Elanco).
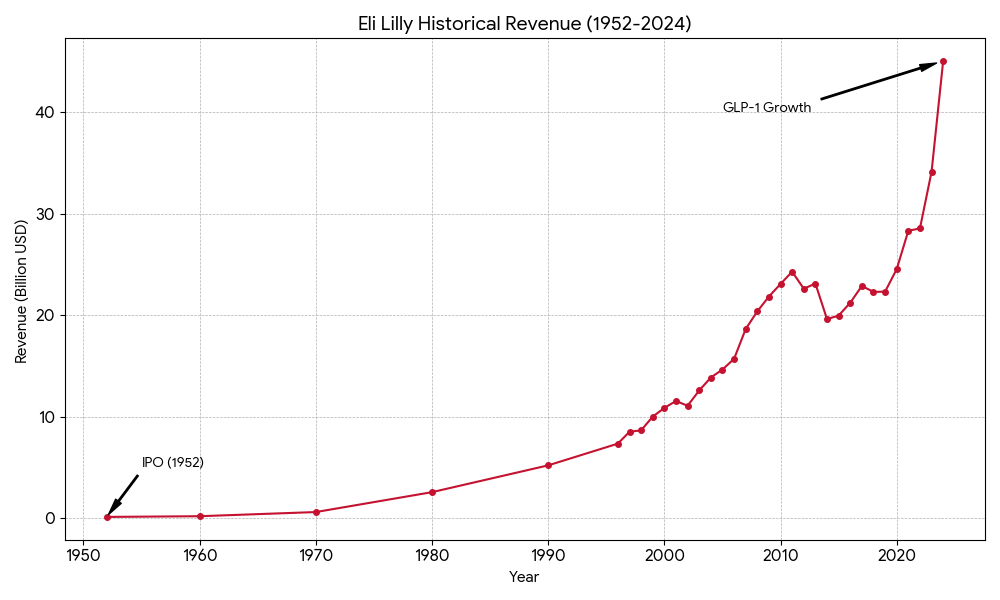
IPO Year: Eli Lilly went public in 1952 on the New York Stock Exchange. Before this, it was a private family-held corporation.
Revenue Level: Revenue grew from approximately $13M in the 1930s to over $1B by the late 1970s.
Core Products & Sales:
- Iletin (Insulin): Controlled over 70% of the US insulin market for decades.
- Keflex (Cephalexin): An antibiotic that generated over $100M annually by the early 1970s.
Major M&A:
- 1971: Acquired Elizabeth Arden (cosmetics) for $38M. (Later sold in 1987 as the company refocused on healthcare).
4. Biotech and Blockbuster Era (1980s-2000s)
This period was defined by the transition to recombinant DNA technology and the launch of world-famous psychiatric drugs.
- 1982: Launched Humulin, the world’s first human healthcare product created using recombinant DNA technology.
- 1987: Launched Prozac (fluoxetine), which revolutionized the treatment of depression and became a global cultural phenomenon.
- 1996: Launched Zyprexa for schizophrenia, which became one of the company’s top-selling drugs.
Revenue Level: Crossed $5B in 1990; reached $10B by 2000.
Core Products & Sales:
- Prozac (Fluoxetine): Launched in 1987. Peaked at $2.6B in annual sales (roughly 25-30% of total revenue at the time).
- Humulin: The first recombinant DNA drug. Provided steady growth as the first “biotech” blockbuster.
- Zyprexa: Launched in 1996. Peaked at over $4.4B in annual sales by 2003.
Major M&A:
- 1986: Acquired Hybritech for $300M to enter monoclonal antibody research.
- 1994: Acquired PCS Health Systems for $4B (an early attempt at pharmacy benefit management, later sold).
5. Patent Cliffs and Transformation (2010s)
Facing the loss of patent protection for core drugs like Prozac, Zyprexa, and Cymbalta, the company pivoted toward high-growth areas like oncology and immunology.
- 2014: Launched Trulicity (dulaglutide), marking their return to dominance in the diabetes market with GLP-1 therapy.
- Targeted R&D: Invested heavily in Alzheimer’s research despite multiple early-stage setbacks.
Revenue Level: Stagnated between $20B and $24B due to the loss of patents for Prozac, Zyprexa, and Cymbalta.
Core Products & Sales:
- Cymbalta: Peaked at $4.9B in 2012 before patent expiry.
- Alimta: A lung cancer drug generating roughly $2.5B annually during this period.
Major M&A:
- 2008: Acquired ImClone Systems for $6.5B. This brought in Erbitux and established Lilly’s oncology presence.
- 2014: Acquired Novartis Animal Health for $5.4B (later spun off as Elanco in 2019).
- 2019: Acquired Loxo Oncology for $8B (all-cash). This brought in the precision medicine drug Retevmo.
6. The Modern Era: Incretins and Alzheimer’s (2020-Present)
Lilly is currently experiencing its most significant growth phase, driven by metabolic health and neurodegeneration.
- 2023: Mounjaro and Zepbound (Tirzepatide) were approved for diabetes and chronic weight management, making Lilly one of the most valuable companies in the world.
- 2024: Donanemab (Kisunla) received FDA approval for the treatment of early-stage Alzheimer’s disease.
Revenue Level: 2023 revenue was $34.1B. 2025 revenue is projected to exceed $63B due to massive demand for obesity treatments.
Core Products & Sales:
- Mounjaro/Zepbound (Tirzepatide): In Q3 2025, combined sales reached $10.1B in a single quarter, making it the highest-selling drug globally by quarterly volume.
- Verzenio: Breast cancer drug with annual sales exceeding $3B.
Major M&A & Licensing:
- 2023: Acquired DICE Therapeutics for $2.4B (Immunology).
- 2023: Acquired Versanis Bio for up to $1.9B to obtain Bimagrumab (weight loss combo).
- 2023: Acquired Point Biopharma for $1.4B to enter the radiopharmaceutical (cancer) space.
- 2024: Acquired Morphic Therapeutic for $3.2B for oral IBD therapies.
Sources:
