1. Early Exploration and Discovery (1933–1943)
- 1933: The Saudi government signed an oil concession agreement with Standard Oil of California (SoCal, now Chevron). The California Arabian Standard Oil Company (CASOC) was subsequently established to manage development.
- 1938: After years of unsuccessful drilling, a commercial quantity of oil was finally discovered at Dammam Well No.7, famously known as the Prosperity Well.
- 1939: Saudi Arabia exported its first cargo of crude oil, with King Abdulaziz personally turning the valve to start the flow.
Core Technology: Relied on Surface Geologic Mapping and traditional cable-tool drilling. The breakthrough at Dammam No.7 in 1938 utilized Deep-Well Drilling to reach the Arab Zone reservoir at 1,440 meters.
Revenue Level: Minimal. This was a high-risk investment phase. Income was limited to small royalty payments made by CASOC to the Saudi government.
2. Rapid Expansion and the Birth of Aramco (1944–1972)
- 1944: CASOC was officially renamed the Arabian American Oil Company (Aramco).
- 1948: Standard Oil (New Jersey) and Socony-Vacuum (both now part of ExxonMobil) joined as shareholders, forming a partnership of four American oil giants.
- 1950: The Saudi government reached a 50-50 profit-sharing agreement with Aramco. In the same year, the 1,212-kilometer Trans-Arabian Pipeline (Tapline) was completed to transport oil to Europe.
- 1951: The Safaniya field was discovered, which remains the largest offshore oil field in the world.
Core Technology:
- Reservoir Management: Developed large-scale Seawater Injection systems to maintain pressure in the Ghawar field.
- Midstream Engineering: Construction of the Trans-Arabian Pipeline (Tapline), the world’s longest at the time, and the Ras Tanura refinery.
- Offshore Drilling: Pioneered deep-water exploration leading to the discovery of Safaniya (the world’s largest offshore field) in 1951.
Revenue Level: Rapid growth. Following the 1950 “50-50” profit-sharing deal, government oil revenues jumped from 7 million USD in 1939 to over 1 billion USD by the early 1970s.
3. The Nationalization Process (1973–1987)
- 1973: Amid shifting energy politics, the Saudi government acquired a 25% stake in Aramco.
- 1974: The Saudi government increased its ownership stake to 60%.
- 1980: The Saudi government officially acquired 100% ownership of Aramco, marking full control over the nation’s energy resources, though the American companies continued to provide technical management.
Core Technology:
- Master Gas System (MGS): A massive engineering project to capture Associated Gas (previously flared) for domestic power and petrochemicals.
- Early Computer Modeling: Adoption of mainframe computers for basic reservoir simulation.
Revenue Level: Explosive. Driven by the 1973 and 1979 oil price shocks, annual revenues peaked at approximately 100 billion USD in 1980 before declining during the 1980s oil glut.
4. Formation of Saudi Aramco and Transformation (1988–2015)
- 1988: A royal decree officially established the Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco) to take over all operations.
- 1990s: The company began transforming from a pure oil producer into an integrated global energy enterprise by expanding into downstream sectors (refining, marketing, and distribution) and making global investments in Asia, Europe, and the U.S.
- 2000s: Massive development of new fields (such as Khurais and Shaybah) occurred, alongside heavy investment in petrochemicals (e.g., the Petro Rabigh project).
Core Technology:
- TeraPOWERS: Developed proprietary Giga-cell Reservoir Simulation technology, allowing engineers to visualize fluid movement in massive fields with unprecedented detail.
- Maximum Reservoir Contact (MRC): Advanced horizontal and multilateral drilling to increase extraction efficiency.
- Crude-to-Chemicals: Investment in high-conversion refining technologies.
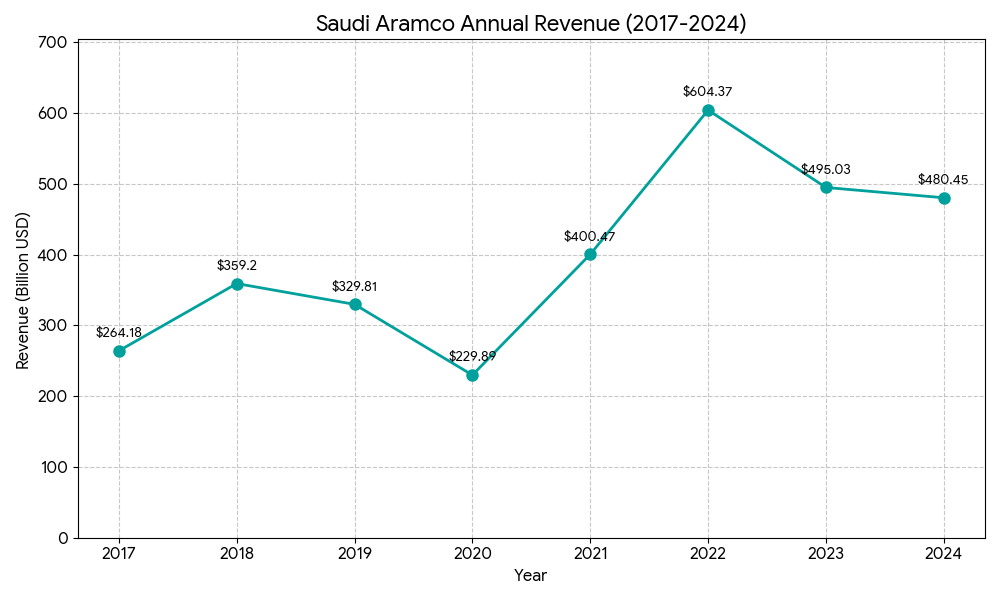
Revenue Level: Mature and Volatile. Revenues generally fluctuated between 200 billion USD and 350 billion USD, highly correlated with Brent Crude prices.
5. Public Listing and Vision 2030 (2016–Present)
- 2016: Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman announced the Saudi Vision 2030 plan, which included the intention to list a portion of the company’s shares.
- 2019: Saudi Aramco launched its Initial Public Offering (IPO) on the Saudi Stock Exchange (Tadawul), raising 25.6 billion USD, making it the largest IPO in history at the time.
- 2020s: The company is currently focusing on a low-carbon transition, including hydrogen energy and carbon capture technology, while continuing to expand downstream investments in key markets like China.
Core Technology:
- IR4.0 & AI: Implementation of Digital Twin technology and AI-driven predictive maintenance in “Lighthouse” facilities like Uthmaniyah and Khurais.
- Sustainability Tech: Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS), blue hydrogen production, and non-metallic materials.
Revenue Level: World-leading.
- 2022: 604 billion USD revenue (Net income: 161 billion USD).
- 2023: 495 billion USD revenue (Net income: 121 billion USD).
- 2024: Approximately 480 billion USD revenue (Net income: 105 billion USD).
Sources:
